×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
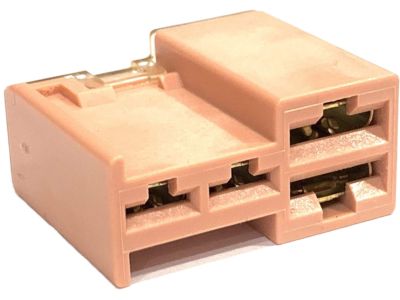
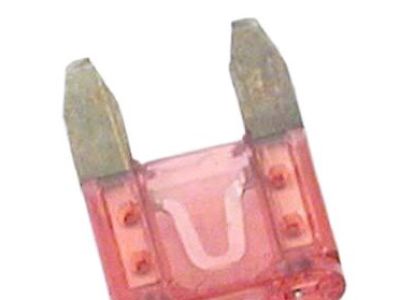
Genuine Nissan Rogue Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
34 Fuses found
Nissan Rogue Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C9902$25.46 MSRP: $38.29You Save: $12.83 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
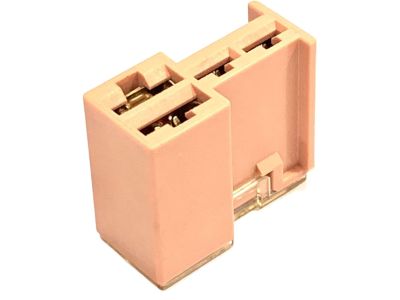
Nissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9900$17.59 MSRP: $26.45You Save: $8.86 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
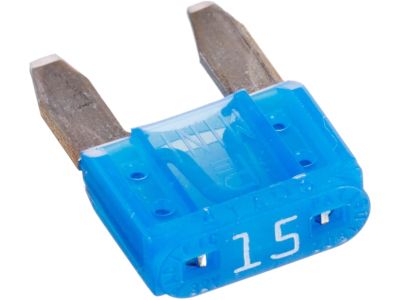
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9910$3.59 MSRP: $5.40You Save: $1.81 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days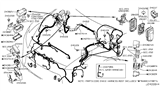
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991B$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C992B$10.71 MSRP: $16.11You Save: $5.40 (34%)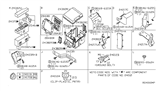
Nissan Rogue Fuse-20A, T-Mini
Part Number: 24319-89920$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9921$20.75 MSRP: $31.20You Save: $10.45 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991A$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days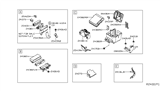
Nissan Rogue Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C9907$21.22 MSRP: $31.91You Save: $10.69 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9915$3.08 MSRP: $4.85You Save: $1.77 (37%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8992C$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89910$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89915$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days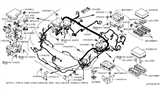
Nissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C992C$9.10 MSRP: $13.69You Save: $4.59 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-79900$28.54 MSRP: $42.93You Save: $14.39 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7995C$17.64 MSRP: $26.53You Save: $8.89 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Rogue Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9904$23.81 MSRP: $35.80You Save: $11.99 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Rogue Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C993B$29.60 MSRP: $44.51You Save: $14.91 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Rogue Fuse-5A
Part Number: 24370-C991A$24.26 MSRP: $36.49You Save: $12.23 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Rogue Fuse
Part Number: 24319-7991A$3.47 MSRP: $5.22You Save: $1.75 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 34 Results
Nissan Rogue Fuse
A Nissan Rogue vehicle incorporates the Fuse as a pivotal safety element which modulates electrical current transmission from the battery and alternator to safeguard electrical components. The Fuse protects electrical components through its ability to block damage inflicted by shocks, vibrations and moisture which maintains proper operation of relays and connected components. Under the hood Nissan Rogue Fuse boxes contain different relays and Fuse whose lifespan reduces due to engine environmental wear. All Nissan Rogue vehicles employ blade Fuse as their main component along with Fuse that use color codes to show electrical amperage ratings. The standard part type applied in present-day automobiles is blade parts although previous models employed glass tube parts. We can separate blade system parts from the other types through their design structure because they provide more options for amperage ratings. Maintaining vehicle features requires regular replacement unit replacement as well as immediate blown replacement part replacement to ensure reliable operation.
If you need any OEM Nissan Rogue Fuse, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Rogue Fuse. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Rogue Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to check and replace fuses, fusible links, and circuit breakers on Nissan Rogue?A:The electrical circuits of the vehicle are protected by fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links While the main fuse/relay panel and the IPDM E/R are situated in the engine compartment on the driver's side near the battery. The interior fuse/relay board is situated in the passenger compartment of your car near the driver side part of the dashboard while the fuse box diagram is written and attached at the rear part of the fuse box cover. Small, medium and large fuses are incorporated in the fuse blocks and these have blade terminal configuration; it may be noted that the medium and large fuses can be pulled with bare hands while, the small fuses have to be removed using pliers or a plastic fuse pulling tool. In case of a failed electrical component, the first thing to consider is the fuse; a test light should then be used to check power at terminal ends; a blown fuse can be ascertained on one side of fuse by absence of power or by appearance. When you replace broken fuses, you must use the right kind of fuses, wrong fuses will affect the protection of circuit. He should check if the cause of immediate blasting of the fuse is due to some other problem such as short circuit; if it is, that has to be solved before replacement of a fuse. Some circuits are protected by fusible links, especially those circuits that have a high current, reside in the fusible link box, which is soldered to the positive battery cable terminal; the scanning must be made before buying a new fusible link box if it is melted. Circuit breakers individually protect some circuits like the power windows, heated seats, and others; If it does not trigger a reset, it means it has overloaded and requires inspection. To perform basic checks on circuit breakers they can be pulled slightly out of their sockets to assess the battery voltage; if voltage is present on only one end the circuit breaker needs to be replaced; some circuit breakers need to be reactivated manually.