×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
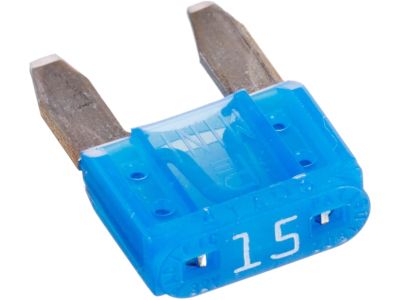
Genuine Nissan Versa Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
25 Fuses found

Nissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9900$17.59 MSRP: $26.45You Save: $8.86 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9910$3.59 MSRP: $5.40You Save: $1.81 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991B$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse-20A, T-Mini
Part Number: 24319-89920$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9921$20.75 MSRP: $31.20You Save: $10.45 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991A$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9915$3.08 MSRP: $4.85You Save: $1.77 (37%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8992C$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89910$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89915$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Versa 50A Fuse
Part Number: 24370-C9924$20.20 MSRP: $30.38You Save: $10.18 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7995C$17.64 MSRP: $26.53You Save: $8.89 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9904$23.81 MSRP: $35.80You Save: $11.99 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-7991A$3.47 MSRP: $5.22You Save: $1.75 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9911$27.71 MSRP: $41.67You Save: $13.96 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7993C$14.23 MSRP: $21.40You Save: $7.17 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7994C$8.26 MSRP: $12.42You Save: $4.16 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-7993A$2.73 MSRP: $4.11You Save: $1.38 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Versa Fuse
Part Number: 24319-7992A$2.95 MSRP: $4.44You Save: $1.49 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 25 Results
Nissan Versa Fuse
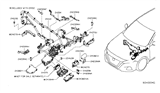
When installed in Nissan Versa vehicles the Fuse operates as an essential safety mechanism that protects electrical components by controlling electrical flow from both the battery and alternator. The protective mechanism of the Fuse blocks excessive electrical flow making sure both relays and connected devices such as radio and headlights maintain proper functionality. The hood contains a Fuse box which stores numerous relays alongside different types and dimensional Fuse. Each Nissan Versa possesses blade Fuse as its standard component since they are common among modern automobiles and differ by size and color to display amperage ratings. Glass tube Fuse found their place in earlier Nissan Versa versions until 1981 when they were no longer applied. The primary separation of these system part types exists through their different designs and uses and blade replacement units show higher capacity for amperage selection. The electrical system of the vehicle requires periodic maintenance as well as quick replacement part replacement to function correctly.
If you need any OEM Nissan Versa Fuse, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Versa Fuse. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Versa Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How are the electrical circuits of a Nissan Versa safeguarded, and what steps should be taken when a fuse or circuit breaker fails?A:Almost all electrical circuits employed in the operation of the vehicle are protected by fuses, circuit breakers as well as fusible linkages; the main fuse relay is situated in the engine bonnet on the driver's side in front of the battery, and the interior fuse/relay is positioned within the passenger compartment to the left and below the steering column. Different types of fuses are small fuses, medium fuses, and large fuses that are installed in the fuse blocks whereby the small fuses demand a tool and commonly known as fuses pullers made up of pliers or a mini plastic fuse puller. After an electrical component is problematic, one has to observe the fuse first since the element between the terminals which melts whenever a fuse is blown can be easily spotted; the existence of power at the exposed terminal ends is confirmed by using a test light. Faculty from a different rating with the blown fuse jeopardizes circuit protection, so it is vital to use the correct kind of fuse. If a replacement fuse blinks out as soon as it has been placed, then the problem that prompted the blown fuse, common one being a short circuit, should be fixed before another replacement is made. Some of the circuits also have fusible links and these areas include high current areas which can be replaced with links of the same amperes after removing the negative cable of the battery. Circuit breakers guard individual circuits like the power windows or the heated seats, that automatically pop and reset when there is an overload; if it does not, it requires immediate check. A simple form of test is when the CB is slightly withdrawn from the socket, one may probe with a voltmeter to check if battery voltage is available at both ends; often if it is not, then replacement is necessary and some types of circuit breakers may have to be reset physically.