×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Nissan Armada Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
24 Fuses found
Nissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C991B$10.41 MSRP: $15.65You Save: $5.24 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9900$17.59 MSRP: $26.45You Save: $8.86 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9910$3.59 MSRP: $5.40You Save: $1.81 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991B$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days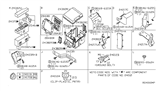
Nissan Armada Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C9906$27.37 MSRP: $41.16You Save: $13.79 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse-20A, T-Mini
Part Number: 24319-89920$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9921$20.75 MSRP: $31.20You Save: $10.45 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991A$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9915$3.08 MSRP: $4.85You Save: $1.77 (37%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8992C$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89910$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Armada Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89915$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C992C$9.10 MSRP: $13.69You Save: $4.59 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days

Nissan Armada Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C9912$2.36 MSRP: $3.55You Save: $1.19 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7995C$17.64 MSRP: $26.53You Save: $8.89 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9911$27.71 MSRP: $41.67You Save: $13.96 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7993C$14.23 MSRP: $21.40You Save: $7.17 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7994C$8.26 MSRP: $12.42You Save: $4.16 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Armada Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-7996C$13.35 MSRP: $20.07You Save: $6.72 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 24 Results
Nissan Armada Fuse
If you need any OEM Nissan Armada Fuse, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Armada Fuse. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Armada Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How are the electrical circuits of a Nissan Armada safeguarded and what should be considered when replacing fuses and fusible links?A:Of protection for the electrical circuits in the vehicle, there is an incorporated assortment of fuses, circuit breakers and fusible links, whereas the principal fuse/relay plate is located at the engine compartment, and the interior fuse/relay plate is situated in the passenger compartment. Every fuse serves a relevant circuit and it comes with an identifier that is always placed at the fuse panel. Small, medium and large firses are used and they all have the same blade terminal arrangement; however while the medium and large fuses can be removed by finger the small ones have to be removed by pliers or a small plastic fuse puller. Whenever an electrical component fails it is always recommended that one should check the fuse first, and use a test light to probe for power on the terminal ends and if found that the fuse has been blown then one can use his or her eyes to check of the element in the fuse is melted. Besides, it is vital to replace the blown fuses with the suitable type of fuse to ensure appropriate protection of the circuit is provided. More often, if an individual replacement fuse blows as soon as it is inserted, the problem is a short circuit resulting from faulty wiring, and the problem should be looked into before applying another fuse. Also, some circuits are protected with fusible links especially for high current applications, and these once it gets a highest current it is meant to melt. While replacing a blown fusible link one should use one of the same specifications; if it blows again it is circuit trouble shooting and then fit new link.