×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Nissan Maxima ABS Sensor
ABS Wheel Speed Sensor- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
43 ABS Sensors found

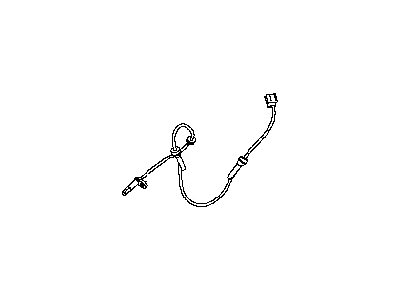
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-ANTISKID, FRONTNT
Part Number: 47910-3TA2A$189.52 MSRP: $280.62You Save: $91.10 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days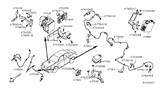
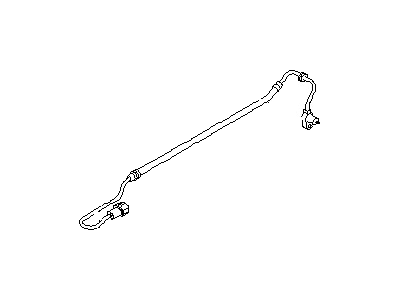
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID,Front
Part Number: 47910-JA000$136.24 MSRP: $254.97You Save: $118.73 (47%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days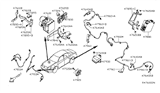
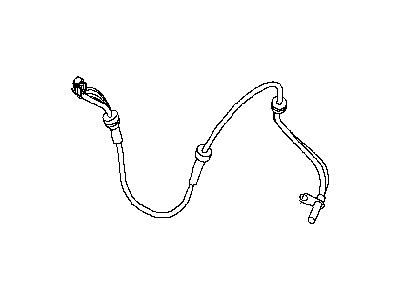
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly Anti Ski, Rear
Part Number: 47900-ZX70A$197.40 MSRP: $292.28You Save: $94.88 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days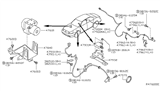
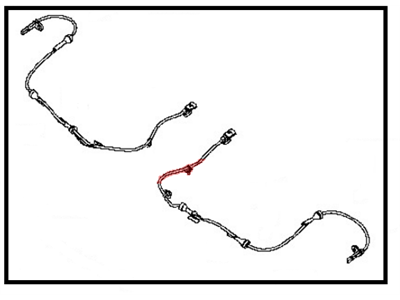
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID,Front LH
Part Number: 47911-7Y000$162.35 MSRP: $240.38You Save: $78.03 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly Anti Ski, Rear
Part Number: 47901-ZX70A$219.96 MSRP: $325.70You Save: $105.74 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days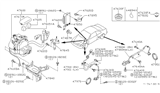
Nissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47901-0L700$222.39 MSRP: $328.92You Save: $106.53 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47900-7Y000$117.68 MSRP: $170.43You Save: $52.75 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID,Front RH
Part Number: 47910-7Y000$162.35 MSRP: $240.38You Save: $78.03 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID, Front
Part Number: 47910-3TA1A$189.52 MSRP: $280.62You Save: $91.10 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47901-7Y000$296.36 MSRP: $452.32You Save: $155.96 (35%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days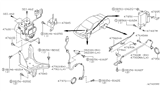
Nissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47900-5Y705$162.47 MSRP: $223.78You Save: $61.31 (28%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID,Front RH
Part Number: 47910-5Y700$140.28 MSRP: $198.13You Save: $57.85 (30%)Nissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-ANTISKID,REARR
Part Number: 47900-3TA2A$221.71 MSRP: $328.28You Save: $106.57 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID,Front RH
Part Number: 47910-5Y705$133.97 MSRP: $198.13You Save: $64.16 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysNissan Maxima Sensor Assembly-Anti SKID,Front LH
Part Number: 47911-2Y000$128.77 MSRP: $190.43You Save: $61.66 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysNissan Maxima Abs Sensor Rear R
Part Number: 47900-86E01$297.11 MSRP: $438.85You Save: $141.74 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47901-9N00A$219.96 MSRP: $325.70You Save: $105.74 (33%)Nissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47900-9N00A$197.40 MSRP: $292.28You Save: $94.88 (33%)Nissan Maxima Anti Skid Sensor Assembly Rear
Part Number: 47900-5Y700$158.44 MSRP: $223.78You Save: $65.34 (30%)
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 43 Results
Nissan Maxima ABS Sensor
If you need any OEM Nissan Maxima ABS Sensor, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Maxima ABS Sensor. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Maxima ABS Sensor Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What is the purpose and functionality of the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) on Nissan Maxima?A:ABS still gets to control the brake line pressure so that equally the turnability, the direction stability as well as the rate of deceleration are maintained when severe brakes are applied and on most types of surfaces so that each wheel rotation is checked in turn. Actuator assembly includes an electric hydraulic pump and three solenoid valves for the wheels as to supply hydraulic pressure to the braking system. The current that these speed sensors pick from each wheel is sine wave current, and it travels to the ABS control unit, the brain of this system that compares current wheel speed with normal speed and controls hydraulic pressure to prevent lock-up. The control unit also performs a self-test when the vehicle exceeds four mph and the ABS warning light will flicker. If the warning light is on, it means the system requires attention, although the determination of the problem is not always straightforward, but to get a DTC, certain procedures vary with year, make, and model. The basic checks are aimed at checking brake fluid, electrical connection, fuses, and brake parts. If there are trouble codes, then by grounding a certain terminal, it can be cleared and for the warning light to remain on, professional help should be sought.
Related Nissan Maxima Parts
Browse by Year
2023 ABS Sensor 2022 ABS Sensor 2021 ABS Sensor 2020 ABS Sensor 2019 ABS Sensor 2018 ABS Sensor 2017 ABS Sensor 2016 ABS Sensor 2014 ABS Sensor 2013 ABS Sensor 2012 ABS Sensor 2011 ABS Sensor 2010 ABS Sensor 2009 ABS Sensor 2008 ABS Sensor 2007 ABS Sensor 2006 ABS Sensor 2005 ABS Sensor 2004 ABS Sensor 2003 ABS Sensor 2002 ABS Sensor 2001 ABS Sensor 2000 ABS Sensor 1999 ABS Sensor 1998 ABS Sensor 1997 ABS Sensor 1996 ABS Sensor 1995 ABS Sensor 1994 ABS Sensor 1993 ABS Sensor 1992 ABS Sensor 1991 ABS Sensor 1990 ABS Sensor 1989 ABS Sensor