×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Nissan Maxima Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
29 Fuses found
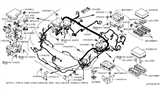
Nissan Maxima Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C991B$10.41 MSRP: $15.65You Save: $5.24 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9900$17.59 MSRP: $26.45You Save: $8.86 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9910$3.59 MSRP: $5.40You Save: $1.81 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days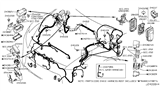
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991B$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C992B$10.71 MSRP: $16.11You Save: $5.40 (34%)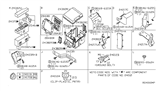
Nissan Maxima Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C9906$27.37 MSRP: $41.16You Save: $13.79 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse-20A, T-Mini
Part Number: 24319-89920$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9921$20.75 MSRP: $31.20You Save: $10.45 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8991A$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9915$3.08 MSRP: $4.85You Save: $1.77 (37%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-8992C$4.20 MSRP: $6.31You Save: $2.11 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89910$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89915$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan Maxima Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C992C$9.10 MSRP: $13.69You Save: $4.59 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days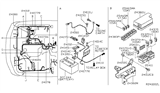
Nissan Maxima Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9980$26.59 MSRP: $40.96You Save: $14.37 (36%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
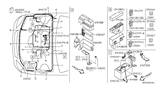
Nissan Maxima 50A Fuse
Part Number: 24370-C9924$20.20 MSRP: $30.38You Save: $10.18 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days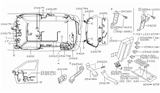
Nissan Maxima Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9907$3.64 MSRP: $5.47You Save: $1.83 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Maxima Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C993B$29.60 MSRP: $44.51You Save: $14.91 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Maxima Fuse-5A
Part Number: 24370-C991A$24.26 MSRP: $36.49You Save: $12.23 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 29 Results
Nissan Maxima Fuse
If you need any OEM Nissan Maxima Fuse, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Maxima Fuse. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Maxima Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What are fuses and how do they protect electrical circuits in Nissan Maxima?A:The electrical circuits of the vehicle are protected by a combination of fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links, with fuse blocks located under the instrument panel on the left side of the dashboard and in the engine compartment, including a second engine compartment fuse box for 2007 and later models. Power can be checked at the exposed terminal tips of each fuse; if power is present at one side but not the other, the fuse is blown, which can also be identified by visual inspection as the element between the terminals melts. It is essential to replace blown fuses with the correct type, as fuses of different ratings are physically interchangeable, but only the proper rating should be used to ensure each electrical circuit receives the specific amount of protection needed, with the amperage value molded into the fuse body. If a replacement fuse immediately fails, it should not be replaced again until the underlying issue, often a short circuit caused by a broken or deteriorated wire, is isolated and corrected. Some circuits, such as the ignition circuit, are protected by fusible links, which are located in the engine compartment fuse block next to the battery and are larger than standard fuses. To replace a fusible link, the negative cable from the battery must first be disconnected, followed by unplugging the burned-out link and replacing it with a new one, while also determining the cause of the overload that melted the original link before installation.
Related Nissan Maxima Parts
Browse by Year
2023 Fuse 2022 Fuse 2021 Fuse 2020 Fuse 2019 Fuse 2018 Fuse 2017 Fuse 2016 Fuse 2014 Fuse 2013 Fuse 2012 Fuse 2011 Fuse 2010 Fuse 2009 Fuse 2008 Fuse 2007 Fuse 2006 Fuse 2005 Fuse 2004 Fuse 2003 Fuse 2002 Fuse 2001 Fuse 2000 Fuse 1999 Fuse 1998 Fuse 1997 Fuse 1996 Fuse 1995 Fuse 1994 Fuse 1993 Fuse 1992 Fuse 1991 Fuse 1990 Fuse 1989 Fuse 1988 Fuse 1987 Fuse 1986 Fuse 1985 Fuse