×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Nissan 350Z Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
9 Fuses found
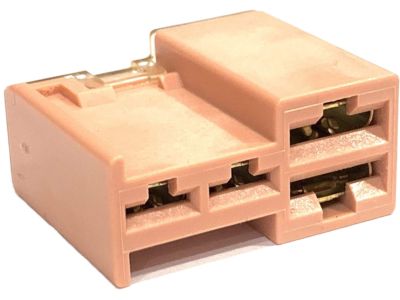
Nissan 350Z Connector Assembly - FUSIBLE Link
Part Number: 24370-C9902$25.46 MSRP: $38.29You Save: $12.83 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
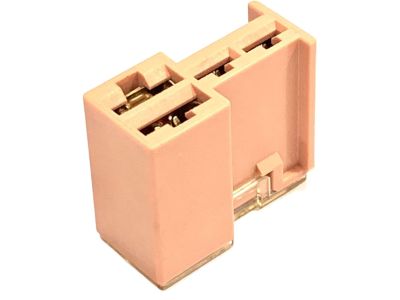
Nissan 350Z Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9900$17.59 MSRP: $26.45You Save: $8.86 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan 350Z Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9910$3.59 MSRP: $5.40You Save: $1.81 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan 350Z Connector Assy-Fusible Link
Part Number: 24370-C9921$20.75 MSRP: $31.20You Save: $10.45 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan 350Z Fuse
Part Number: 24319-C9915$3.08 MSRP: $4.85You Save: $1.77 (37%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan 350Z Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89910$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan 350Z Fuse
Part Number: 24319-89915$4.00 MSRP: $6.02You Save: $2.02 (34%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Nissan 350Z 50A Fuse
Part Number: 24370-C9924$20.20 MSRP: $30.38You Save: $10.18 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan 350Z Fuse
If you need any OEM Nissan 350Z Fuse, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan 350Z Fuse. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan 350Z Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How are the electrical circuits of a Nissan 350Z protected, and How to accessing and replace fuses and fusible links?A:Electrical connections of the vehicle consist of fuses as well as Relays which are in two areas the engine corner fuse as well as relay box in the right rear corner of the engine room area together with the battery. To get to the smaller fuse and relay box, which is situated in the lower right corner of the vehicle, one has to open the battery cover; however, getting to the bigger box requires the removal of the cowl trim panel. However, to the author's knowledge, there is a third position of the fuse box located at the interior of the car behind a small cover on the left side of the kick panel. The larger box located in the engine compartment is the Intelligent Power Distribution Module in other words else it is called the fuse and relay box. Different fuses for different circuits are used and there are mini and maxi fuses of which the maxi are usually located in the fuse and relay box. For removing the majority of fuses, it is necessary to use electronics needle-noise pliers or a small plastic fuse-puller, while a test light is useful for checking them. Differences are also pointed out relating to the type of fuses particularly when it comes to replacing fuses that have blown; it should be noted that it is important to replace a fuse with the exact type in order to avoid circuit protection problems. It is important to check the problem that resulted in a replacement fuse because if another one is placed and fail right away, it is probably due the short circuit in wiring. Any wiring between the battery and the alternator, Ignition Switch and any other high load circuits have wiring protection by fusible links which are in appearance but are of higher amperages than a standard fuse. When replacing the fusible link, the negative cable of the battery has got to be removed and besides doing this the user has got to ensure that he or she determines why the specific link has been fused.