×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
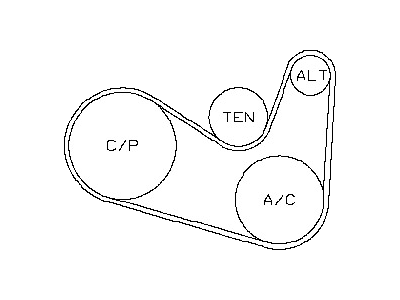
Genuine Nissan Juke Drive Belt
Serpentine Belt- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
4 Drive Belts found
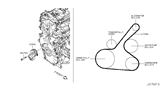
Nissan Juke Alternator Belt
Part Number: 11720-1KC0A$56.85 MSRP: $82.33You Save: $25.48 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Juke Alternator Belt
Part Number: 11720-BV80A$48.01 MSRP: $69.53You Save: $21.52 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Juke Alternator Belt
Part Number: 11720-BV80B$45.73 MSRP: $69.53You Save: $23.80 (35%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Juke Alternator Belt
Part Number: 11720-1KC0B$56.85 MSRP: $82.33You Save: $25.48 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Juke Drive Belt
The Nissan Juke Drive Belt is one of the highly critical parts that play an important role in the Nissan Juke cars. This serpentine Drive Belt links the engine to other units like the alternator and the A/C compressor so as to ensure that these works as required. The Nissan Juke Drive Belt usually comes with 100,000 miles and replacing this component would be in extreme circumstances, that the belt is worn and damaged admiring fraying and cracking around it. Different Juke models make the use of different kinds of Drive Belt, V-belts and multi-groove belts, each and every kind of belts are designed to increase traction and reduce the slippage hence improving the general efficiency. Timing belts with teeth are also incorporated to enhance the overall performance of the engine, this demonstrates the company's creed of innovation. The Nissan Juke Drive Belt is one component that keeps the vehicle as efficient as possible and increases the element of safety because engine and part faults could happen at any time. That it applies to various Juke models proves that it is suitable and efficient in the automotive industry. Also, it is notable that the modern Drive Belt developments also show concern with the improvements of Nissan's performance and the elements' sturdiness. In general, Nissan Juke Drive Belt can be considered a durable and efficient part with its importance for the car that proves its worth as a sturdy and dependable compact crossover SUV model.
If you need any OEM Nissan Juke Drive Belt, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Juke Drive Belt. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Juke Drive Belt Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What does Nissan recommend regarding the renewal of the belt and automatic tensioner, and how should the auxiliary drivebelt be inspected and renewed on Nissan Juke?A:Nissan recommends renewing the belt whenever it is removed, along with the automatic tensioner, and suggests that both should be replaced every 90,000 miles or 6 years, regardless of their condition. The auxiliary drivebelt is located on the right-hand side of the engine and should be inspected periodically due to its susceptibility to failure over time. A basic check for obvious faults can be performed from the engine compartment, but a thorough inspection requires access from below, necessitating the front of the car to be jacked up and supported on axle stands, followed by the removal of the right-hand roadwheel and wheel arch liner. With the engine off, inspect the entire length of the drivebelt for cracks and separation of the plies, turning the engine to move the belt for a complete view, while also checking for fraying and glazing, as well as inspecting the pulleys for any damage. To renew the belt, turn the tensioner clockwise to release tension, then lift the drivebelt from the pulleys, noting its fitted position. If the belt is removed, it must be renewed. Unbolt the tensioner unit and install a new one, ensuring the retaining bolt is tightened to the specified torque. Hold the tensioner clockwise while fitting the new belt around the pulleys, ensuring it is correctly located in the grooves. Rotate the engine several times to check the belt alignment, then reattach the wheel arch liner and roadwheel, lowering the vehicle and tightening the roadwheel nuts to the specified torque.