×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Nissan Parts
- Nissan Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
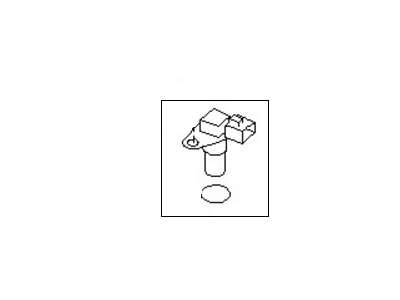
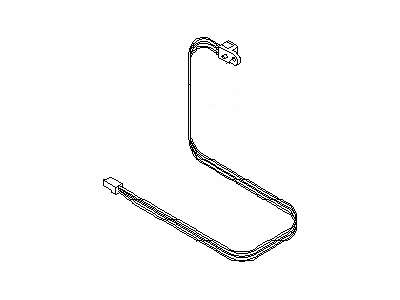
Genuine Nissan Quest Vehicle Speed Sensor
VSS- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
12 Vehicle Speed Sensors found
Nissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-1XF00$184.45 MSRP: $260.52You Save: $76.07 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-8E006$173.47 MSRP: $245.02You Save: $71.55 (30%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days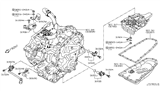
Nissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-X420A$184.45 MSRP: $260.52You Save: $76.07 (30%)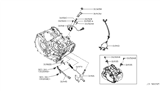
Nissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-8Y000$172.58 MSRP: $243.75You Save: $71.17 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Nissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-X420C$184.45 MSRP: $260.52You Save: $76.07 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days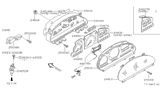
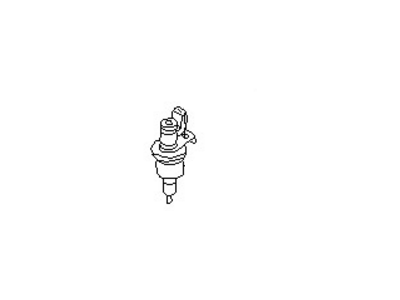
Nissan Quest Sensor-SPEEDOMETER
Part Number: 25015-0B001$87.23 MSRP: $134.40Limited AvailabilityYou Save: $47.17 (36%)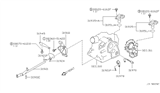
Nissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-8E004$173.47 MSRP: $245.02You Save: $71.55 (30%)Ships in 1 Business DayNissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-80L00$136.18 MSRP: $192.35Limited AvailabilityYou Save: $56.17 (30%)Nissan Quest Sensor-SPEEDOMETER
Part Number: 25015-2Z300$111.17 MSRP: $171.29You Save: $60.12 (36%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysNissan Quest Sensor Assembly-Revolution
Part Number: 31935-80X00$137.10 MSRP: $193.65You Save: $56.55 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days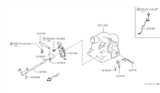
Nissan Quest Vehicle Speed Sensor
If you need any OEM Nissan Quest Vehicle Speed Sensor, feel free to choose them out of our huge selection of genuine Nissan Quest Vehicle Speed Sensor. All our parts are offered at unbeatable prices and are supported by the manufacturer's warranty. In addition, we offer quick shipping to have your parts delivered to your door step in a matter of days.
Nissan Quest Vehicle Speed Sensor Parts Questions & Experts Answers
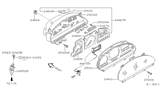
- Q: What steps should be taken if tests indicate that a vehicle speed sensor is functioning properly but issues persist on Nissan Quest?A:If tests show that a sensor is working fine and is not handling any driveability problem or trouble code, check the wiring harnesses and connectors between the said sensor and PCM for any shorts or opens. If there is no problem identified, it is also wise to have the car checked by a dealer's service section or any automobile repair center. The VSS is a pickup coil, variable-reluctance type, attached to the transaxle case; this unit produces a sine-wave AC voltage, with the frequency being a direct function of vehicle speed. The PCM uses the signal from the sensor for different operations of the engine and the transmission and the signal from VSS serves as a power source for the speedometer on the instrument cluster. These are due to varied reasons including multiple driveability and transmission problems that emanate from a malfunctioning VSS, depiction of sensor faults and trouble codes by the Electronic Engine Control system. To check the VSS, remove its connector and switched on the ignition without starting the car, then check the voltage between the sensor's wire connector and ground, should be about of 1 to 5 volts in one of the wires of the sensor. If this is the case, unbolt the VSS and attach an AC Volts meter to it to read for voltage pulsing during the spinning of the sensor drive gear; absence of voltage pulsing, the sensors should be replaced. For replacement, safely lift the vehicle on jack stands, then loosen the negative cable from the VSS and unbolt and then remove the hold down bolt and clamp and the take out the VSS from transaxle. Take out the O-ring on the sensor and check it for damage, if installing a new sensor use a new O-ring. In the same order as removal, reinstallation starts with the uppermost processed layer.
Related Nissan Quest Parts
Browse by Year
2017 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2016 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2015 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2014 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2013 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2012 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2011 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2010 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2009 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2008 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2007 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2006 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2005 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2004 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2003 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2002 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2001 Vehicle Speed Sensor 2000 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1999 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1998 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1997 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1996 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1995 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1994 Vehicle Speed Sensor 1993 Vehicle Speed Sensor